Understanding the TLS Handshake: Securing Your Online Connection 🔒
In this post, we’ll dive into the intricacies of the TLS Handshake, a process that plays a crucial role in establishing secure communications between you and the websites you visit. We aim to unlock the mystery surrounding the coveted padlock icon you see in your browser, which indicates that your connection is secure.
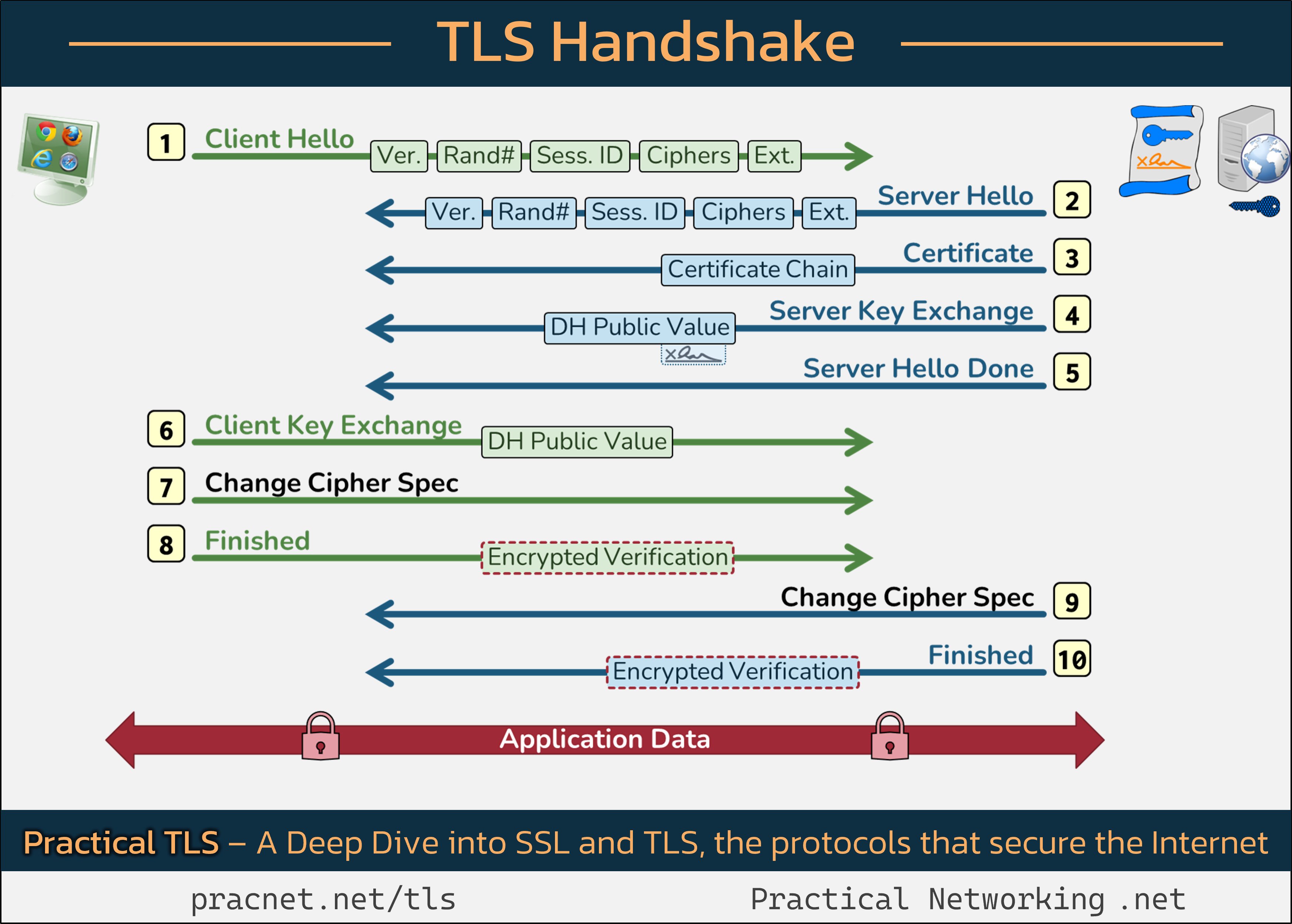
For a clear visual representation of the TLS Handshake, it might be useful to have this infographic open in another tab as you read through the details:
Introduction: The Purpose of TLS
Before we delve into the handshake itself, it’s essential to remember two primary objectives of SSL/TLS:
- ✅ Authenticate the Server’s Identity: Ensuring that the server is truly who it claims to be.
- ✅ Establish Session Keys: Securing the data transferred between the client and the server.
Key Concepts to Understand
To fully grasp the TLS Handshake, you should be familiar with some core cryptographic concepts, though we won’t dive deep into them here. If needed, explore more about:
With that foundation, let’s break down the records that comprise the TLS Handshake.
Step 1: Client Hello
The handshake begins with a Client Hello message sent from your web browser. This initial communication contains five critical fields:
- SSL Version: The highest version of SSL/TLS supported by the client.
- Random Number: A unique 32-byte random value generated by the client.
- Session ID: Utilized for potential session resumption.
- Cipher Suites: A list of cryptographic algorithms that the client can support.
- Extensions: Additional features that enhance the handshake process.
Diving Deeper into the Client Hello
- SSL Version: The client shares the highest SSL version it can support. The server responds with its own supported version, and both parties will typically agree on the highest common version. Presently, only TLS
Share this content:




Great overview of the TLS handshake process! If you’re experiencing issues with the secure padlock icon not appearing in your browser, it could be related to SSL/TLS certificate configuration or server support. Here are some troubleshooting steps you can try:
If you find that your configuration is correct but issues persist, consider updating your server Software and ensuring your hosting environment supports current security standards. Feel free to share specific error messages or symptoms for more tailored assistance!