Understanding the TLS Handshake: Unlocking the Secrets Behind Secure Browsing 🔒
In the ever-evolving landscape of internet security, understanding how our data is protected is more important than ever. Today, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the TLS Handshake—the process that establishes a secure connection between your web browser and the websites you visit, resulting in that reassuring padlock icon in your browser’s address bar.
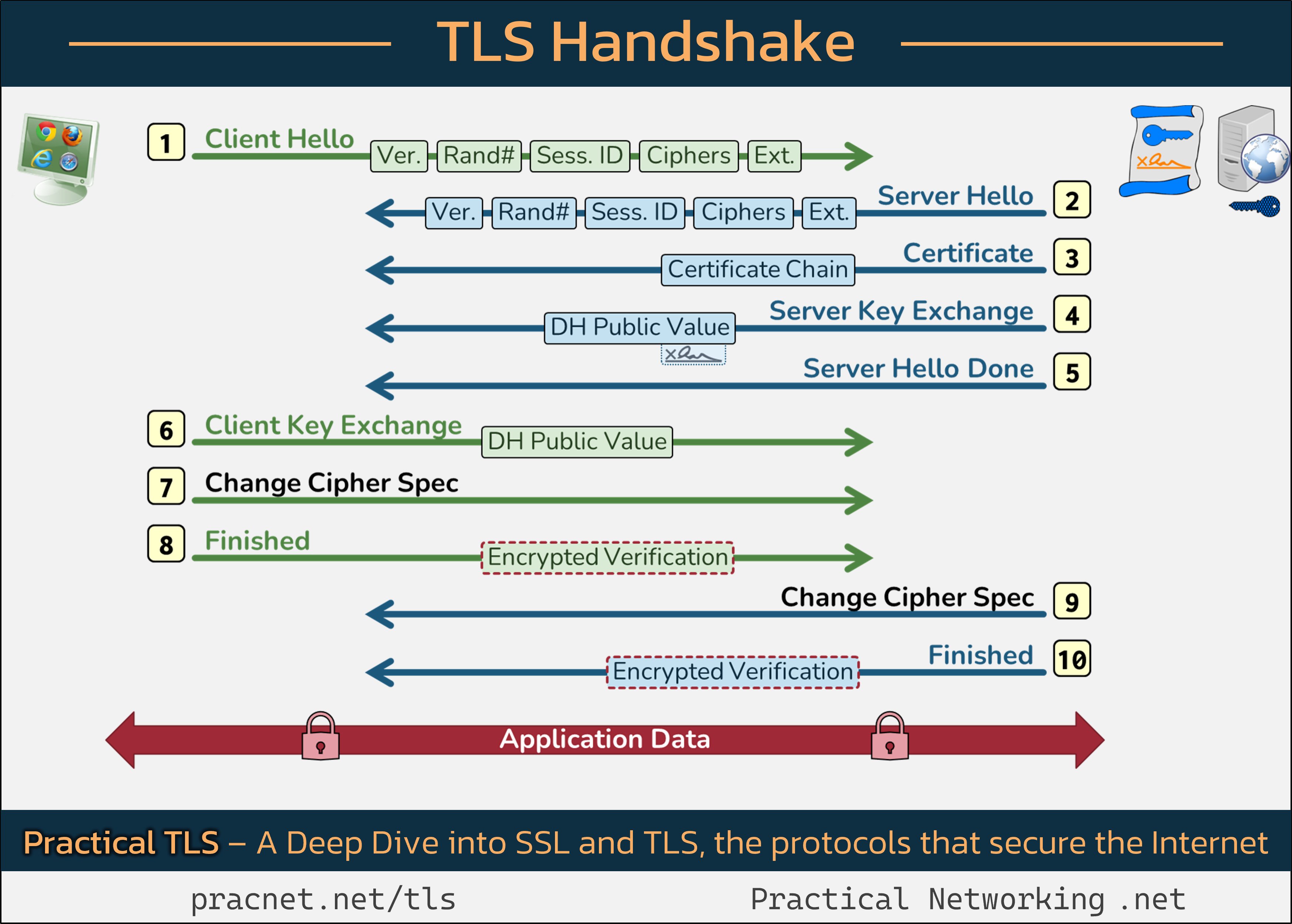
To help illustrate this process, we’ll reference an informative infographic that you may find useful as we navigate through the various stages of the handshake. Feel free to open it in another tab for a visual aid during our discussion:
The Purpose of TLS / SSL
Before we dive into the handshake itself, it’s important to note that the primary goals of TLS (Transport Layer Security) are twofold:
- ✅ Authentication: Ensures that the server is indeed who it claims to be.
- ✅ Data Protection: Establishes session keys to secure data transmission.
A Quick Clarification: Records vs. Packets
As we work through the handshake process, keep in mind that each distinct step or message is referred to as a “Record.” This should not be confused with a “Packet,” as several Records can exist within a single Packet, or vice versa.
Key Cryptographic Concepts
To fully grasp the TLS Handshake, familiarize yourself with the following cryptographic fundamentals:
While we won’t delve deeply into these concepts today, understanding them will certainly enhance your comprehension of the handshake process.
The Stages of the TLS Handshake
Now, let’s break down the steps involved in the TLS Handshake:
1️⃣ Client Hello
The handshake commences with the Client (your web browser) sending a Client Hello message. This message contains five crucial fields:
- SSL Version
- Random Number
- Session ID
- Cipher Suites
- Extensions
These fields work together to facilitate a secure connection.
SSL Version: The
Share this content: