Understanding the TLS Handshake: What Happens Before You Get that Secure Padlock 🔒
When you click on an HTTPS link and see that reassuring padlock icon, you might not think about the complex series of interactions that secure your connection. In this post, we will dive into the intricacies of the TLS handshake—the vital process that helps establish a secure session between your web browser and the server of the website you’re accessing.
For a clearer understanding, we recommend checking out this informative infographic that maps out every step of these interactions: 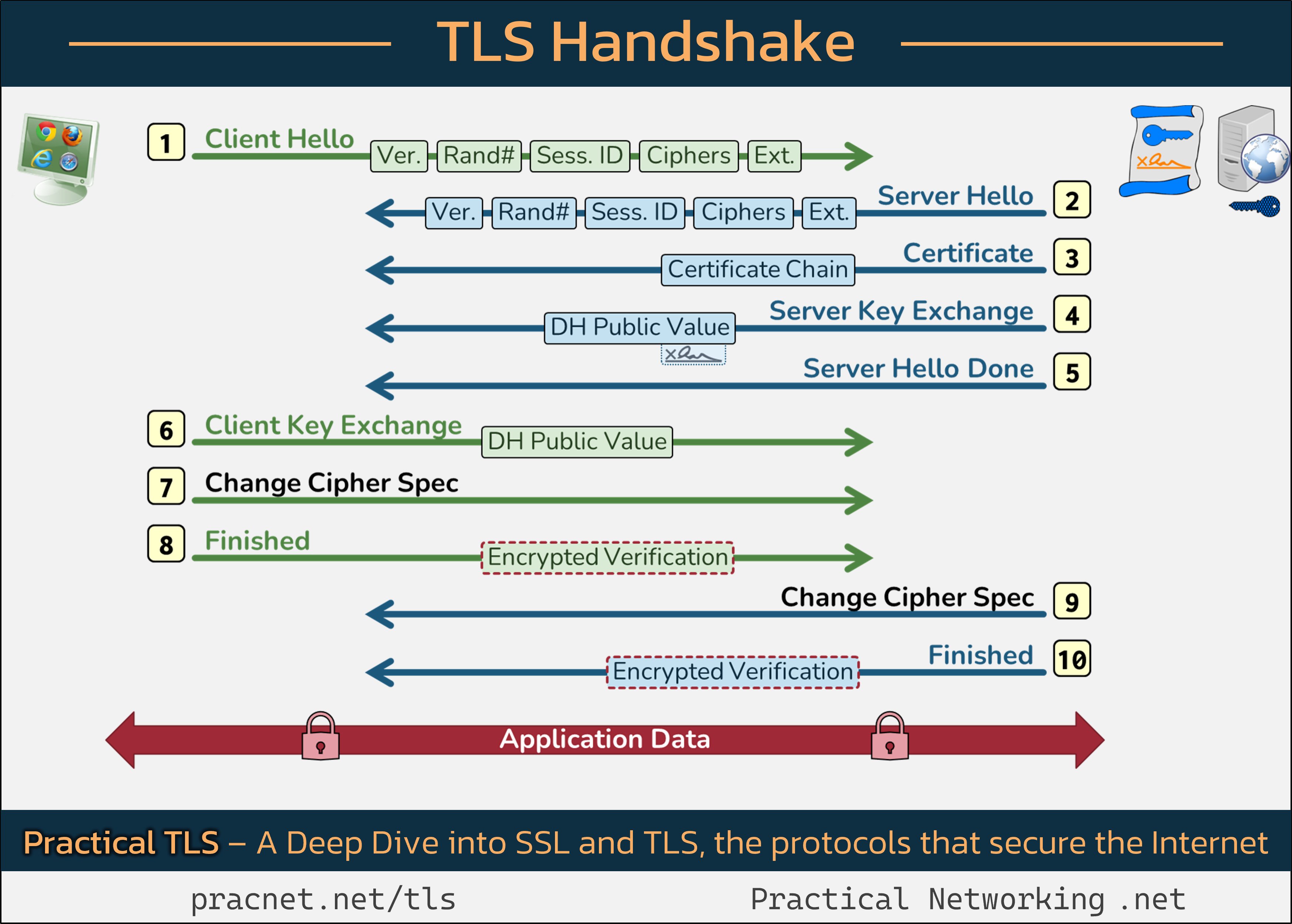
Overview: The Purpose of SSL/TLS
Before we jump into the details, it’s essential to recognize that the primary goals of SSL/TLS protocols are:
- ✅ To authenticate the server, ensuring it is genuinely who it claims to be
- ✅ To generate session keys that secure data during transfer
Key Considerations Before the Handshake
Records vs. Packets
When analyzing the infographic, keep in mind that each line represents a Record within the TLS handshake. Records differ from Packets, as multiple Records can fit into one Packet or vice versa.
Cryptography Basics
To fully grasp the TLS handshake, familiarity with key cryptographic concepts is beneficial, including:
These terms are not the focal point of our discussion, but a quick review of the linked materials can provide a solid foundation.
The Steps of the TLS Handshake
1️⃣ Client Hello
The handshake commences with the Client Hello message from your web browser, which contains the following critical components:
- SSL Version
- Random Number
- Session ID
- Cipher Suites
- Extensions
Each of these fields is crucial for establishing a secure connection.
SSL Version: The client indicates the highest SSL version it supports (e.g., SSL 3.0, TLS 1.2). The server does the same, and
Share this content:



