Understanding the TLS Handshake: The Journey to a Secure Web Connection
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring a safe browsing experience is more crucial than ever. One of the key components of internet security is the TLS handshake, a process that secures your communication with websites through encryption. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what occurs between you and the website you’re visiting to achieve that reassuring padlock icon in your browser’s address bar. 🔒
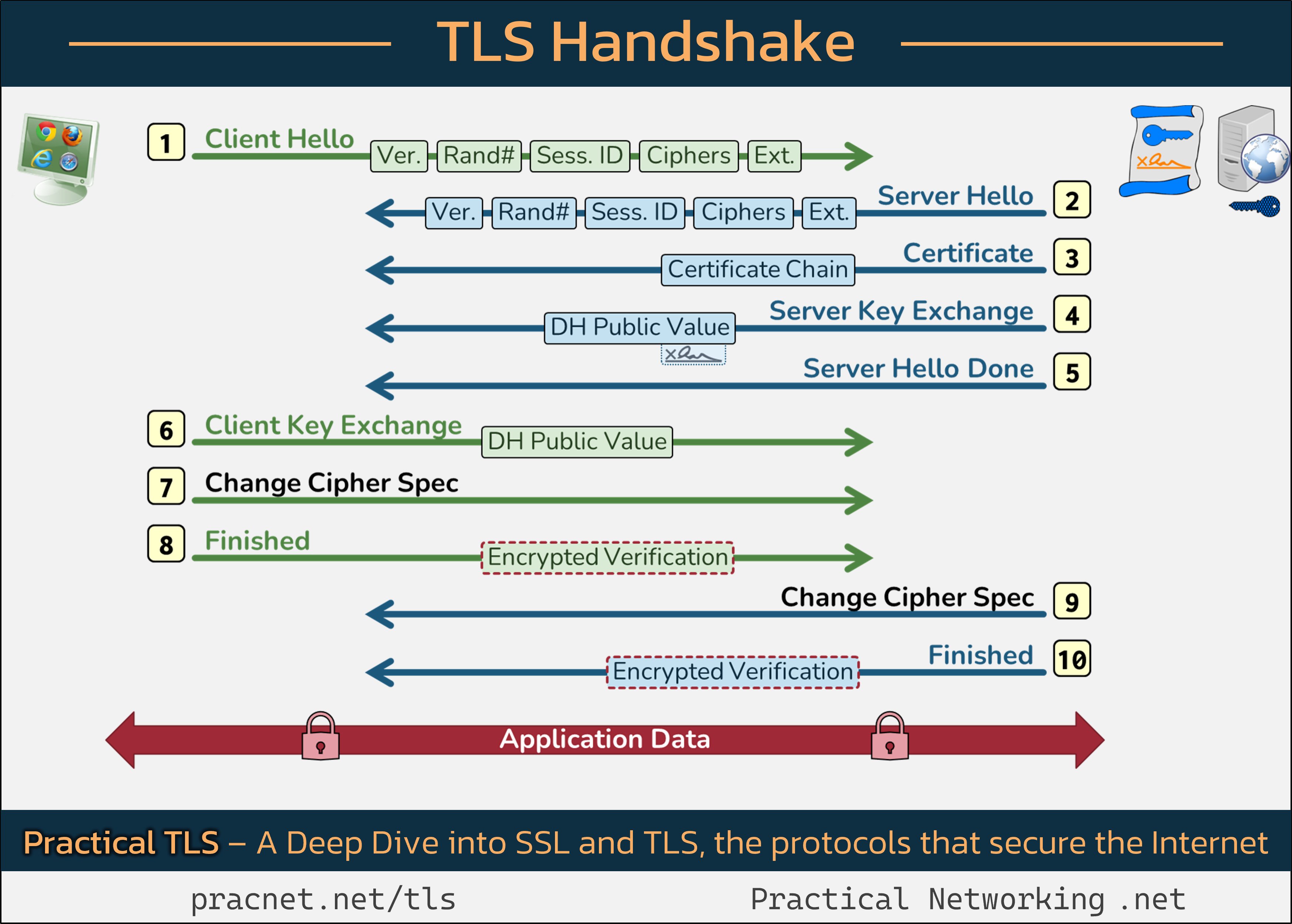
To aid our exploration, we’ll reference a helpful infographic that outlines the various messages exchanged during the handshake. You might find it beneficial to have this image open in another tab as you read along.
Image source: Twitter
What is the TLS Handshake?
The primary objective of SSL/TLS protocols is to verify the server’s authenticity and to establish secure session keys that will safeguard the data transmitted over the connection. Before looking into the details of the handshake process, it’s essential to clarify two concepts that often create confusion:
Records vs. Packets
In the TLS context, a “Record” refers to each message sent during the handshake process. This is distinct from a “Packet,” as multiple Records can be packed into a single Packet, or conversely, a single Record may require several Packets for delivery.
Cryptographic Fundamentals
A basic understanding of certain cryptographic principles is beneficial for grasping the details of the TLS handshake:
While we won’t delve into these concepts in depth, feel free to explore the linked videos for a deeper understanding.
The TLS Handshake Process
Let’s unpack the series of events that constitute the TLS handshake:
1. Client Hello
The process begins with the Client—your web browser—sending a “Client Hello” message, which contains five critical fields:
- SSL Version: Indicates the highest version of SSL/TLS supported by the client.
- Random Number: A 32-byte random value added for security.
- Session ID: Used in session resumption scenarios.
- Cipher Suites:
Share this content: