Troubleshooting a Non-Starting PC: When Your Build Won’t Power On
Experiencing a computer that refuses to turn on can be a frustrating ordeal, especially when all typical troubleshooting steps seem to lead nowhere. In this article, we’ll explore a real-world case involving a modern PC setup with no response at startup—no fans spin, no lights, nothing—and provide insights into potential causes and solutions.
System Overview
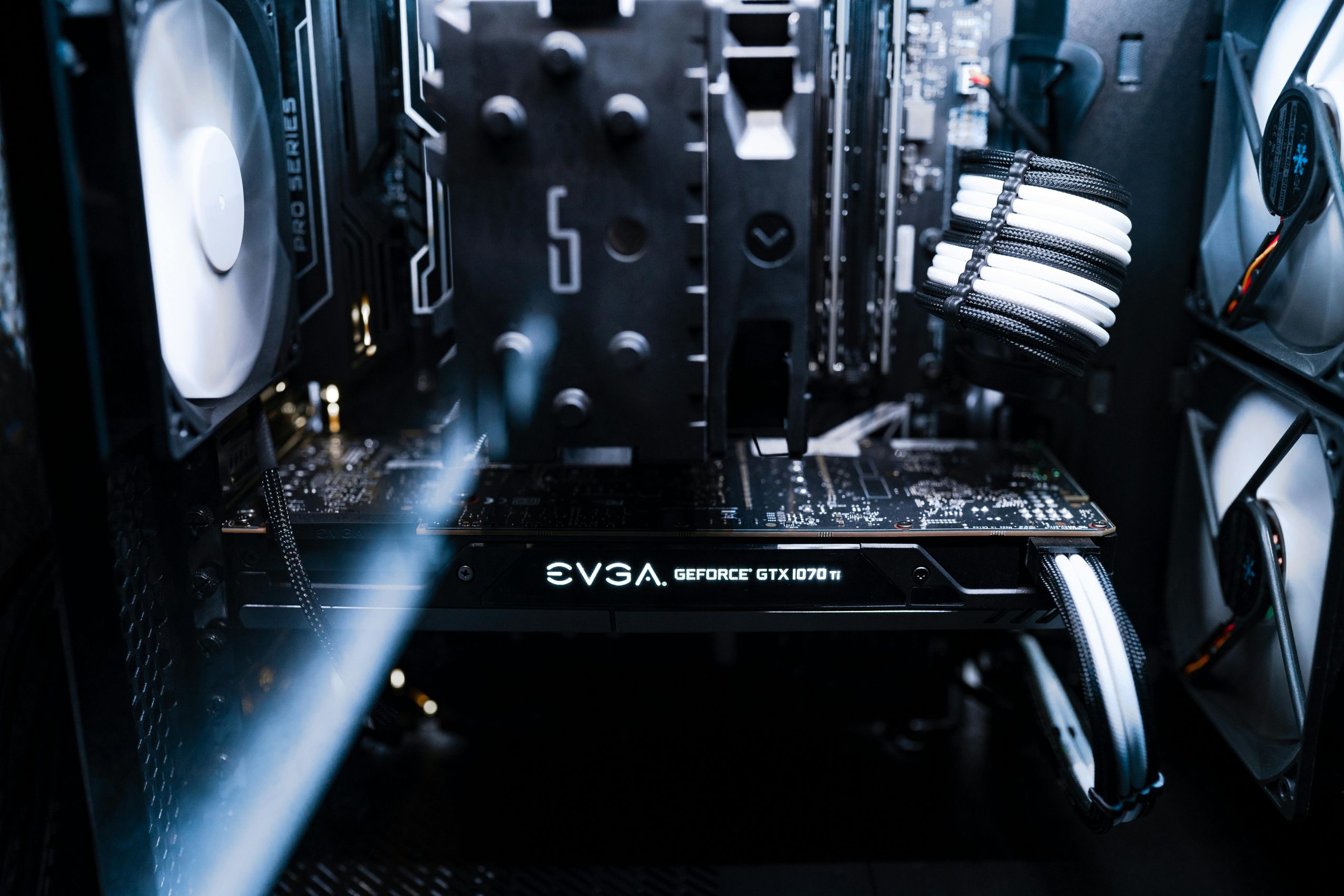
The affected system features:
- Processor: AMD Ryzen 5 5600GT
- Motherboard: Gigabyte B450M DS3H V3
- Memory: 16GB DDR4 XPG D45 RAM (single module)
- Graphics: No dedicated graphics card
- Storage: 500GB Crucial NVMe SSD, 128GB SATA SSD, 1TB Seagate HDD
- Power Supply: 500W 80+ White PSU
All components were purchased brand new on December 24, making age less likely as an issue.
The Issue
Initially, the PC wouldn’t respond when powered on. Basic troubleshooting such as switching outlets, replacing power cables, and testing with a different power source yielded no results. The situation persisted even after moving the PC to different outlets, indicating the problem was not purely electrical.
Seeking professional assistance, the individual took the system to a repair shop. The repair technicians swapped the PSU, but the system still refused to start. In a further attempt, they removed the processor (which was stuck to the heatsink), reseated all components, and surprisingly, the system powered on. This suggested a possible connection or contact issue.
Reapplying thermal paste and reseating heatsinks, the PC worked temporarily but failed to respond the next morning. It was then taken to the original vendor’s repair service, where advanced troubleshooting was performed over a week. After multiple tests, including component checks and bench tests, the technicians could not identify a definitive fault. The system resumed functioning intermittently, only to revert to the non-starting state later.
Key Observations and Diagnostics
-
No response when pressing the power button: Indicating potential issues with power delivery or motherboard/PSU communication.
-
No signs of overheating: During the working period, CPU temperatures remained within normal ranges, even under load (max ~80°C), ruling out thermal shutdown causes.
-
Component reseating: Removing and reinstalling parts temporarily restored functionality
Share this content: