Understanding the TLS Handshake: Unlocking the Secrets to Secure Connections 🔒
In this post, we will take a detailed look into the process that secures your online interactions with that reassuring padlock icon. The TLS (Transport Layer Security) handshake is a critical mechanism that ensures a safe connection between your web browser and the server you’re visiting.
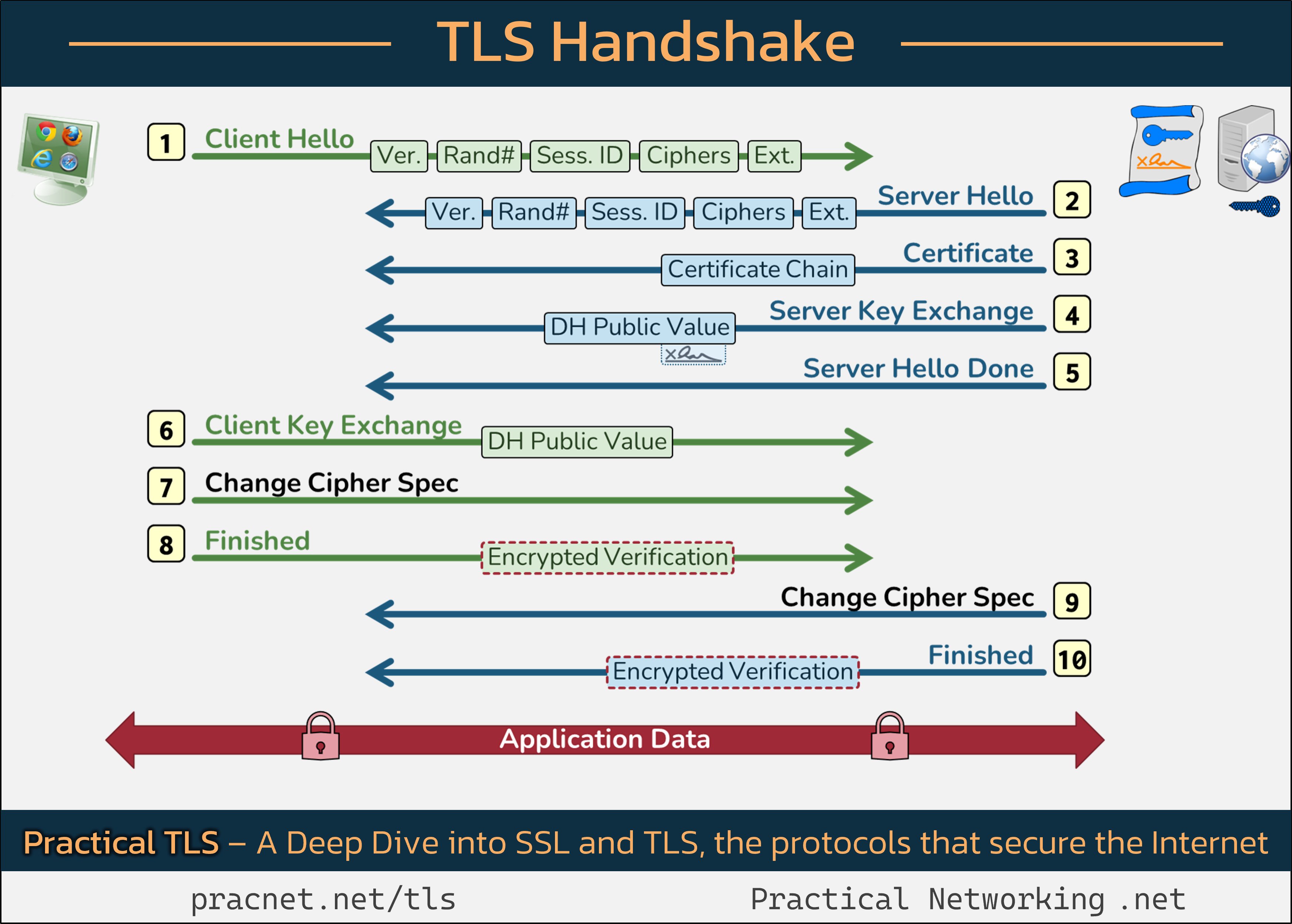
Visual Guide
To enhance your understanding, I recommend opening the following infographic in a new tab as we discuss the various stages of the handshake process:
This image visually represents the exchanges between the Client (your web browser) and the Server (the website you are connecting to) during a TLS session initiation.
The Foundations of SSL/TLS
Before we dive into the handshake itself, it’s essential to understand that the primary objectives of SSL/TLS are two-fold:
- ✅ Confirm the Server’s identity
- ✅ Establish secure Session Keys for data protection
Let’s clarify two key concepts that will aid your comprehension of the handshake process:
Records vs. Packets
In the context of the TLS handshake, each line from the infographic represents a “Record.” It’s important to note that a Record is not synonymous with a Packet. Records can be bundled together within a single Packet, or multiple Packets may be required for a single Record.
Basic Cryptography Concepts
Familiarity with certain cryptographic principles will enhance your understanding of the TLS Handshake, including:
While this post will focus on the handshake mechanics without diving deep into these concepts, I encourage you to explore the linked videos for a more comprehensive understanding.
Step 1: The Client Hello
The TLS Handshake begins with the Client Hello message from your web browser. This message encompasses five crucial fields:
- SSL Version
- Random Number
- Session ID
- Cipher Suites
- Extensions
These fields set the stage for the remainder of the handshake.
1.1 SSL Version
The
Share this content:




Thank you for sharing this detailed post on the TLS handshake process. Understanding how TLS establishes secure connections is vital for both developers and support engineers to troubleshoot connection issues effectively.
If you’re experiencing problems with the TLS handshake—such as failed connections, expired certificates, or security warnings—here are some steps you can take:
Implementing these