Understanding the TLS Handshake: How Your Browsing Achieves Secure Connections
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the security of our online activities is paramount. The presence of that reassuring padlock icon 🔒 on your browser signifies a secure connection between you and the website you’re visiting. But what happens behind the scenes to make this possible? In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the TLS handshake process, the essential steps involved, and the underlying cryptographic principles at play.
To enhance your understanding, it might be useful to reference this detailed infographic that captures the entire handshake sequence: 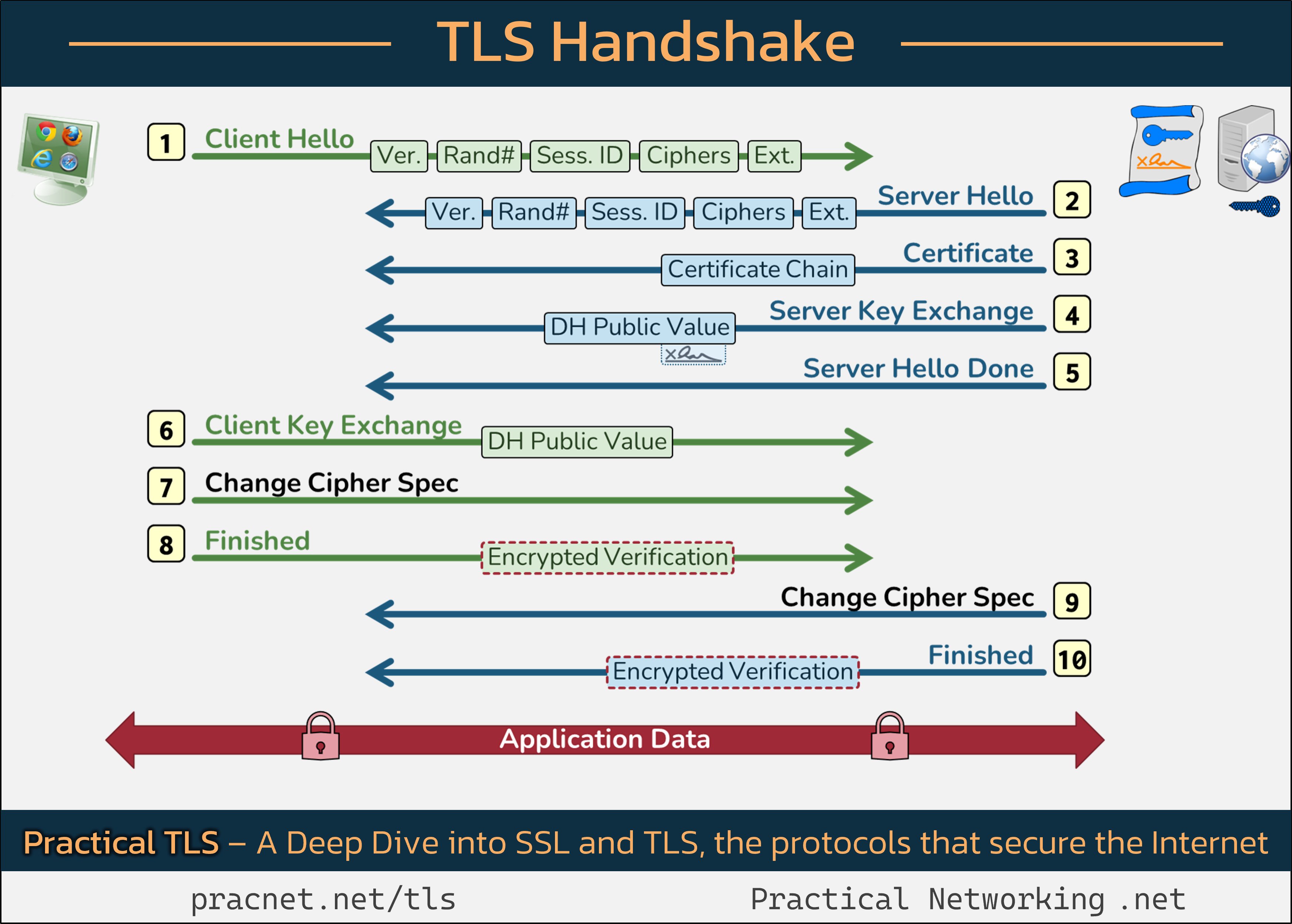
Introduction to TLS: A Brief Overview
Before we dive into the handshake itself, it’s crucial to understand the primary objectives of SSL/TLS protocols:
- ✅ Authentication: To ensure that the server you’re connecting to is legitimate.
- ✅ Session Security: To establish session keys that will encrypt the data exchanged during your browsing session.
Important Concepts to Grasp
As we embark on this discussion, there are two fundamental concepts you should be familiar with:
-
Records vs. Packets: Each interaction during the TLS handshake is categorized as a “Record.” This differs from a “Packet,” as multiple Records can fit into a single Packet, and a single Record might span multiple Packets.
-
Cryptographic Basics: Familiarity with terms like Hashing, MACs and HMACs, and Encryption will enhance your understanding. For the sake of this article, we will focus solely on the handshake process without diving deep into these cryptographic principles.
Now, let’s break down the steps of the TLS Handshake.
1️⃣ Client Hello
The handshake initiates with the Client, which is your web browser, sending a Client Hello message containing five critical fields:
- SSL Version
- Random Number
- Session ID
- Cipher Suites
- Extensions
Each component serves a
Share this content:




Hello, thank you for sharing this detailed overview of the TLS handshake process. Understanding these cryptographic fundamentals is essential for troubleshooting SSL/TLS-related issues effectively.
If you’re experiencing problems with secure connections, here are some steps you can take: