Understanding the TLS Handshake: Achieving That Coveted Padlock 🔒
When you’re browsing the internet, one of the things you look for is the padlock icon in the address bar, indicating a secure connection. Have you ever wondered how your web browser establishes that secure connection? In this post, we will explore the intricate process behind the TLS handshake—from the moment you initiate a connection to the time your data is safely encrypted.
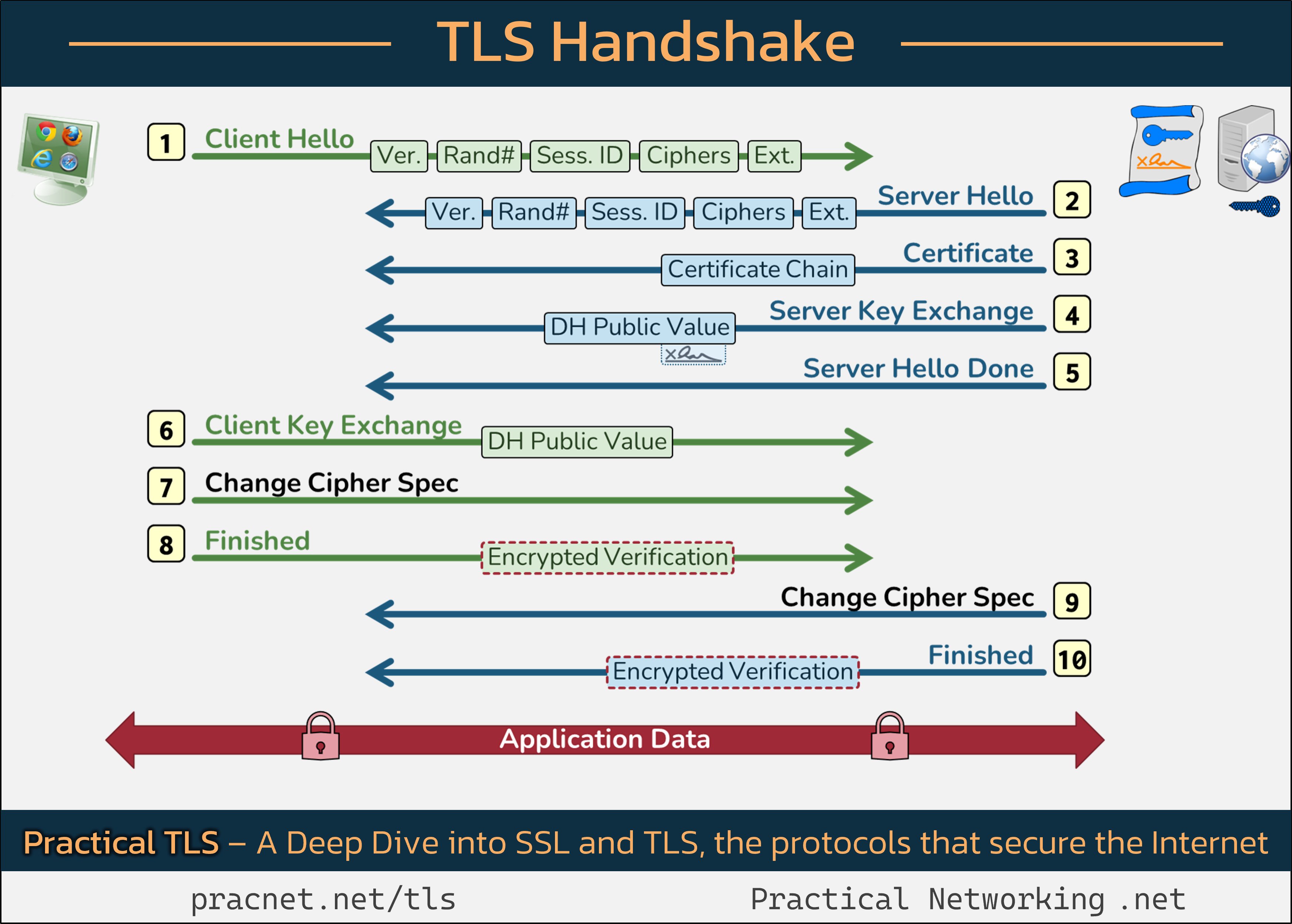
To make our discussion clearer, I recommend keeping the following infographic open in a new tab as we walk through the steps of the handshake:
Setting the Stage
Before diving into the details, it’s crucial to understand two key objectives of SSL/TLS:
- ✅ Authenticate the Server’s identity.
- ✅ Establish session keys to ensure the security of data exchanges.
It’s also important to clarify two fundamental concepts before we unpack the content of the handshake:
Record vs. Packets
When discussing the handshake, each line in the infographic refers to a “Record.” However, these records are not synonymous with packets. Sometimes, multiple records fit into a single packet, while other times, several packets are needed to transmit a single record.
The Role of Cryptography
Familiarity with a few cryptographic principles will enrich your understanding of the TLS handshake:
We won’t delve deeply into these concepts here, allowing us to keep our focus squarely on the handshake process.
Step 1: Client Hello
The TLS handshake commences with the Client Hello message sent by your web browser. This message contains five critical fields:
- SSL Version
- Random Number
- Session ID
- Cipher Suites
- Extensions
Details of the Client Hello Fields
-
SSL Version: The Client identifies the highest version of SSL/TLS it supports. The server will reciprocate with its own supported version, enabling both parties to agree on the highest mutually supported SSL/TLS version.
-
**
Share this content:




Thank you for sharing this informative post on the TLS handshake process. Understanding the detailed steps involved can significantly improve troubleshooting and security practices. If you’re experiencing issues with SSL/TLS connections, here are some general tips that might help:
Understanding the mechanics as explained in your post is a great step towards effective troubleshooting and enhancing your server security. If you need specific guidance on configuring SSL/TLS on your server environment