Understanding the TLS Handshake: Unlocking the Secrets Behind Secure Connections 🔒
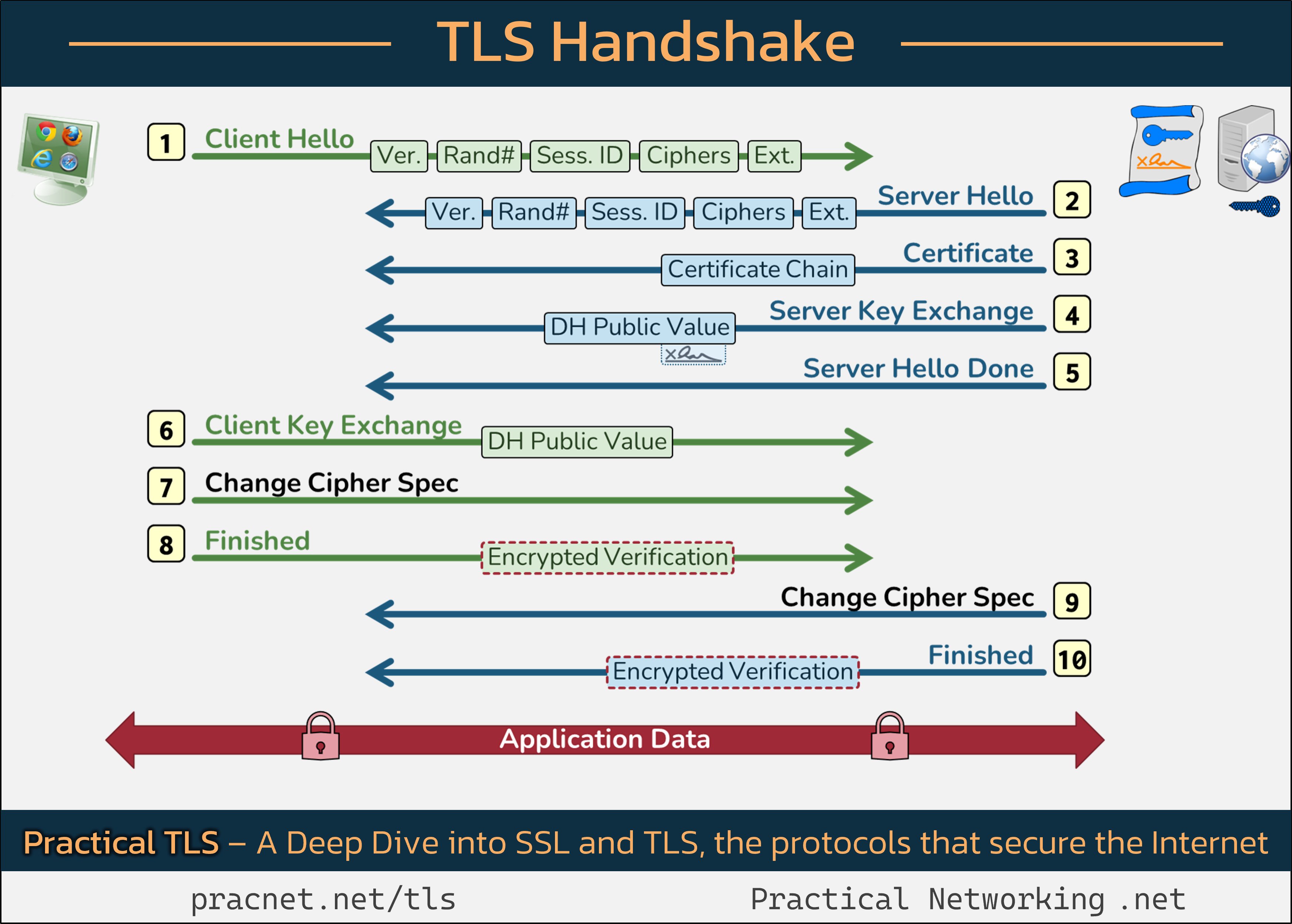
In this post, we will delve into the intricate process that occurs between you and the website you visit to secure your connection and earn that reassuring padlock icon. 🔒 For a visual representation, I recommend opening this infographic in a separate tab for reference as we explore the various stages of the TLS handshake.
Image Source: Twitter
Introduction
The primary objective of SSL/TLS protocols is twofold:
- ✅ Authentication: Ensuring that the server you are communicating with is genuinely who they claim to be.
- ✅ Data Security: Establishing session keys to encrypt and safeguard the information exchanged.
Before we dive into the steps of the handshake process, it is essential to clarify two key concepts:
Records vs. Packets
Each step in the infographic represents a “Record” in the handshake process, which is distinct from a Packet. Multiple records can exist within a single packet, or vice versa, depending on the context.
Cryptographic Basics
A basic understanding of cryptographic principles will enhance your comprehension of the TLS handshake. Key concepts to familiarize yourself with include:
While we won’t dive deeply into these topics here, I encourage you to explore these resources if you find these terms unfamiliar. With that groundwork laid, let’s dissect the records that constitute the TLS handshake.
Step 1: Client Hello
The handshake commences with a Client Hello message initiated by your web browser. This message carries five crucial fields:
- SSL Version
- Random Number
- Session ID
- Cipher Suites
- Extensions
Each of these components plays a vital role in the handshake process.
1.1 SSL Version
The client indicates the highest version of SSL/TLS it supports (e.g., SSL 3.0, TLS 1.2). The server responds with the highest mutually supported version. Currently, only TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 are
Share this content:




Thank you for sharing this detailed overview of the TLS handshake process. Understanding these foundational concepts is essential for troubleshooting secure connection issues. If you’re experiencing problems with SSL/TLS handshakes, here are some steps you can take:
Should you need help diagnosing specific errors or configuring your server settings, please provide details of any error messages you encounter, and I can assist further. Maintaining up-to-date SSL/TLS configurations is vital to preserving secure communications and