Understanding the TLS Handshake: Securing Your Connection 🔒
In the age of digital communication, ensuring your online privacy is paramount. One essential step towards achieving this security is the TLS (Transport Layer Security) handshake, which safeguards the data exchanged between your device and the websites you visit. Here, we will delve into the intricate operations that occur during this handshake process, leading to the familiar padlock icon that signifies a secure connection.
To help visualize this complex procedure, you may find the following infographic useful as you read through the various steps involved in a TLS handshake: 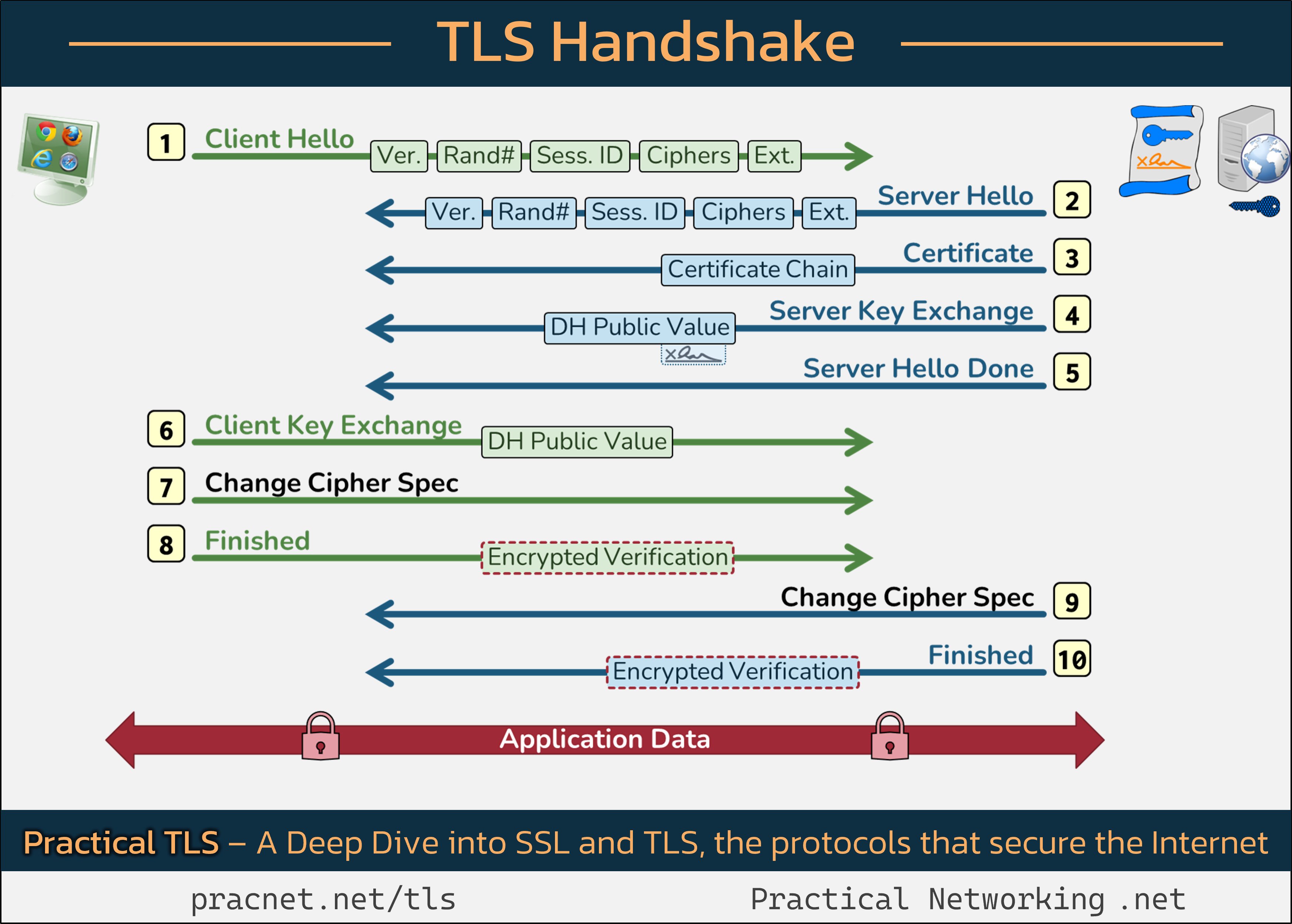
(Image source linked at the end of this post.)
The Purpose of TLS
Before we begin detailing the handshake, it’s important to clarify the two primary objectives of TLS:
- ✅ Authentication: Ensures that the server you are connecting to is legitimate, confirming its identity.
- ✅ Session Key Establishment: Facilitates the creation of session keys to encrypt and protect the data exchanged.
As we embark on this journey through the handshake process, two key concepts are vital to understand:
Records vs. Packets
The infographic outlines “records,” which are the individual messages exchanged during the TLS handshake. It is important to note that these records do not equate to packets; multiple records can fit within a single packet, and alternatively, a record may require multiple packets for transmission.
Cryptographic Foundations
Familiarity with certain cryptographic principles is beneficial for grasping the TLS handshake:
While we won’t delve deeply into these topics here, examining these linked resources will enhance your understanding of the handshake.
Now, let’s break down the records that constitute the TLS handshake.
Step 1: Client Hello
The handshake commences when your web browser, referred to as the Client, sends a Client Hello message. This message comprises five significant fields:
- SSL Version
- Random Number
- Session ID
- Cipher Suites
- Extensions
Each field plays a critical role in
Share this content:




Thank you for sharing this detailed overview of the TLS handshake process. It’s a complex but crucial aspect of securing data in transit. If you’re experiencing issues with SSL/TLS connections, here are some troubleshooting steps you might consider: